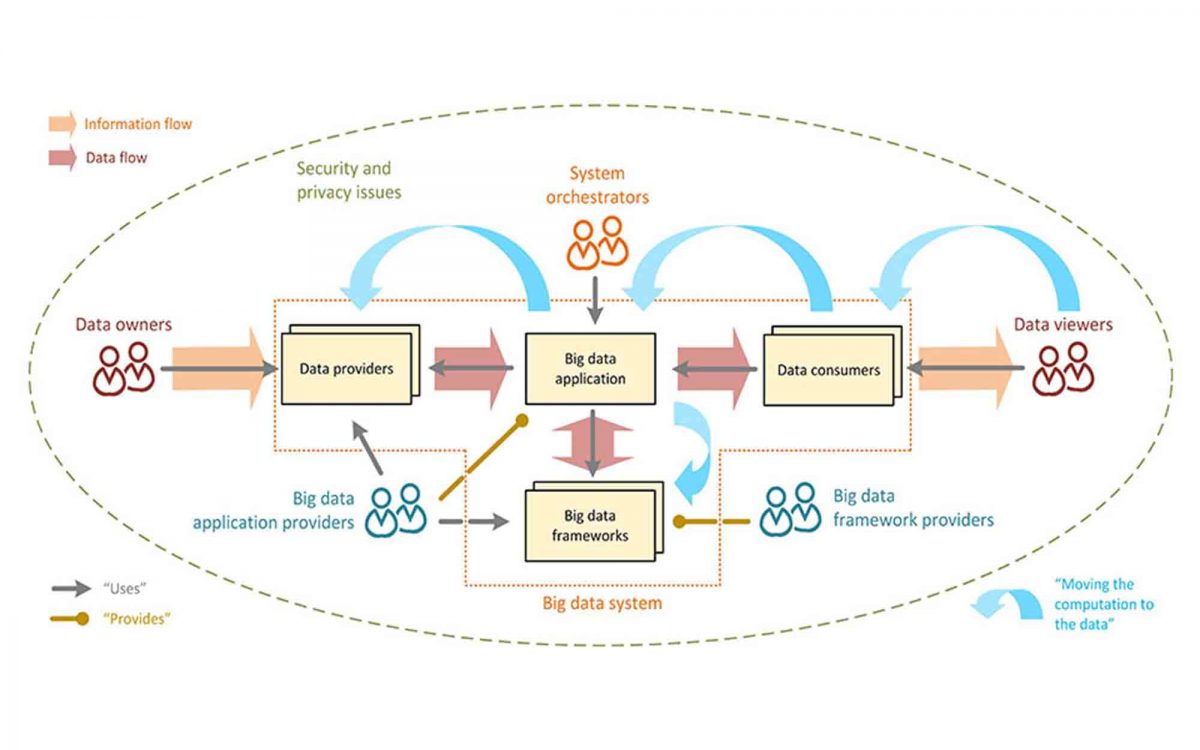
Some visualization principles
Some scientific principles behind how we process visual information. It really helps to understand these principles when you think about how to visualize data.
Proximity. Human beings are by default, see things that are near each other as being together. So for instance, when you look at a scatter plot, we see patterns, right? We see the dots that are all clustered near each other as having something to do with each other. This is just how we recognize patterns.
Next one is Similarity. We see things that look similar and assume that they go together. So this one seems to override proximity, right? So we'll sort of categorize things in this way. Whether similarity is in shape, or in size, or in color.
The next principle is known as Parallelism. The idea here is that we will see parallel lines and assume that they go together or that they have something going on that's similar and the things that aren't parallel, are different, right? And again, this is deep brain science. This is how we all perceive these things.
Proximity. Human beings are by default, see things that are near each other as being together. So for instance, when you look at a scatter plot, we see patterns, right? We see the dots that are all clustered near each other as having something to do with each other. This is just how we recognize patterns.
Next one is Similarity. We see things that look similar and assume that they go together. So this one seems to override proximity, right? So we'll sort of categorize things in this way. Whether similarity is in shape, or in size, or in color.
The next principle is known as Parallelism. The idea here is that we will see parallel lines and assume that they go together or that they have something going on that's similar and the things that aren't parallel, are different, right? And again, this is deep brain science. This is how we all perceive these things.